What is the Packet Slicing of Network Packet Broker?
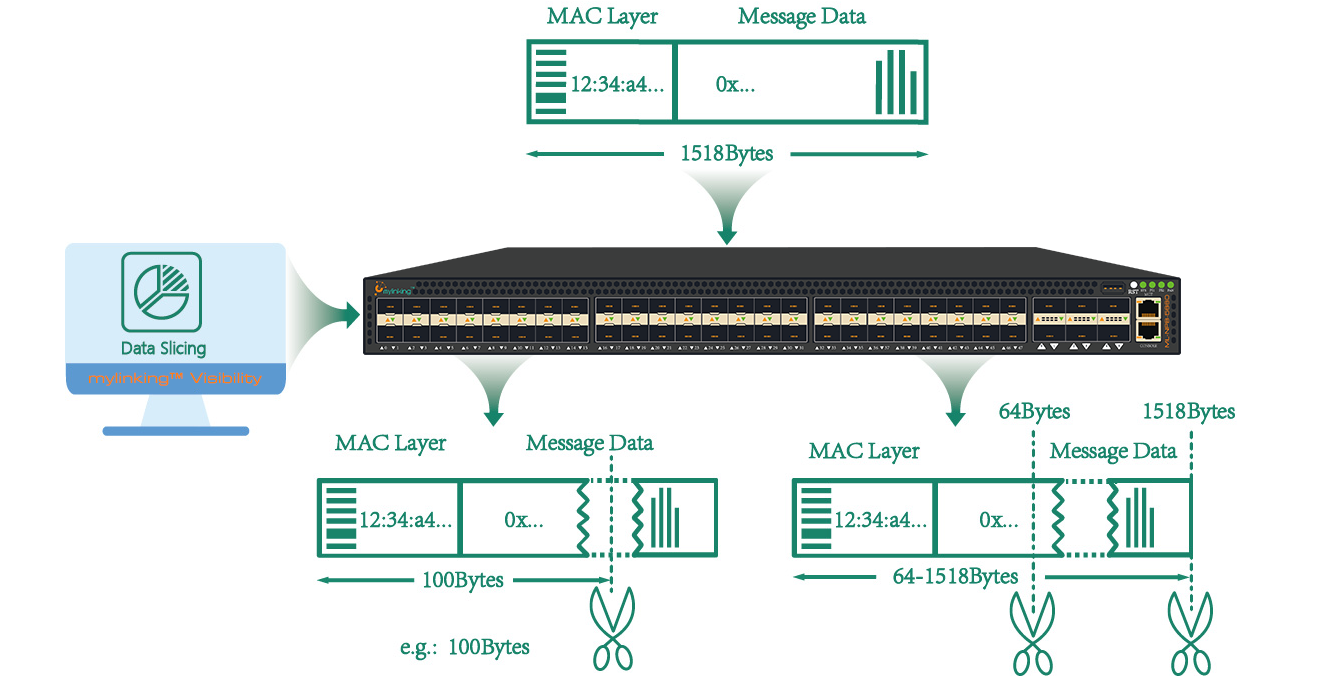
Packet Slicing in the context of a Network Packet Broker (NPB), refers to the process of extracting a portion of a network packet for analysis or forwarding, rather than processing the entire packet. A Network Packet Broker is a device or system that helps manage and optimize network traffic by collecting, filtering, and distributing network packets to various tools, such as monitoring, security, or analysis tools. Packet slicing is used to reduce the amount of data that needs to be processed by these tools. Network packets can be quite large, and not all parts of the packet might be relevant for the specific analysis or monitoring task at hand. By slicing or truncating the packet, unnecessary data can be removed, resulting in more efficient use of resources and potentially reducing the load on the tools.
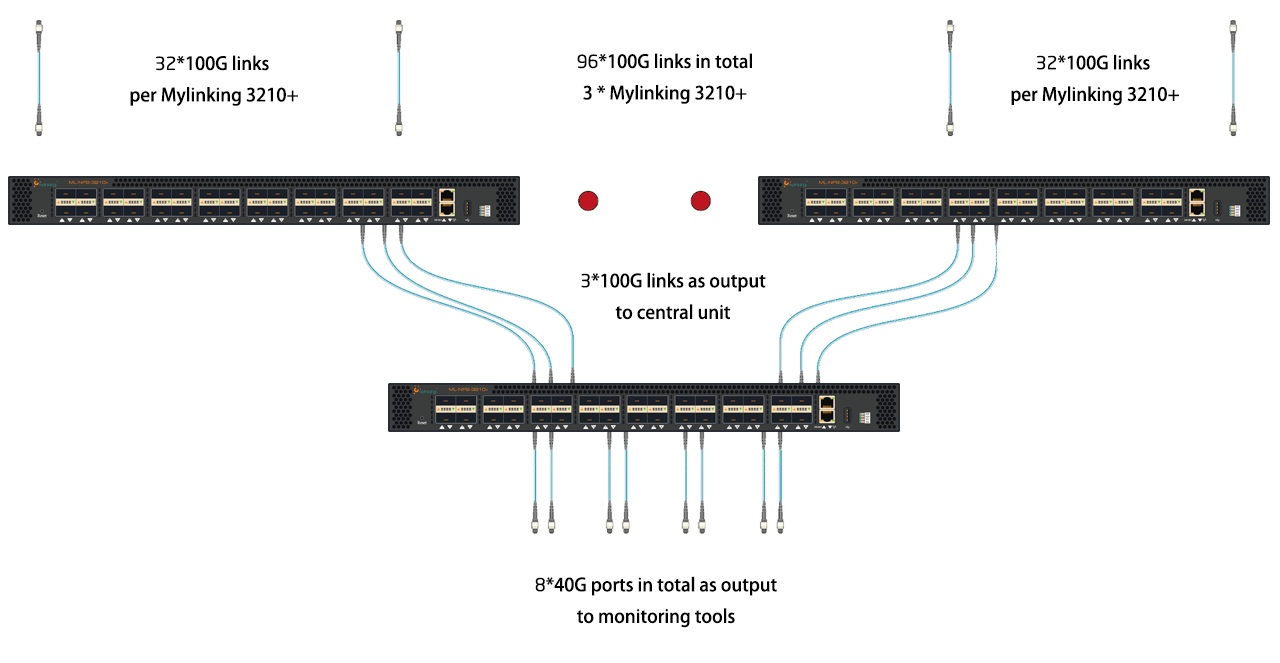
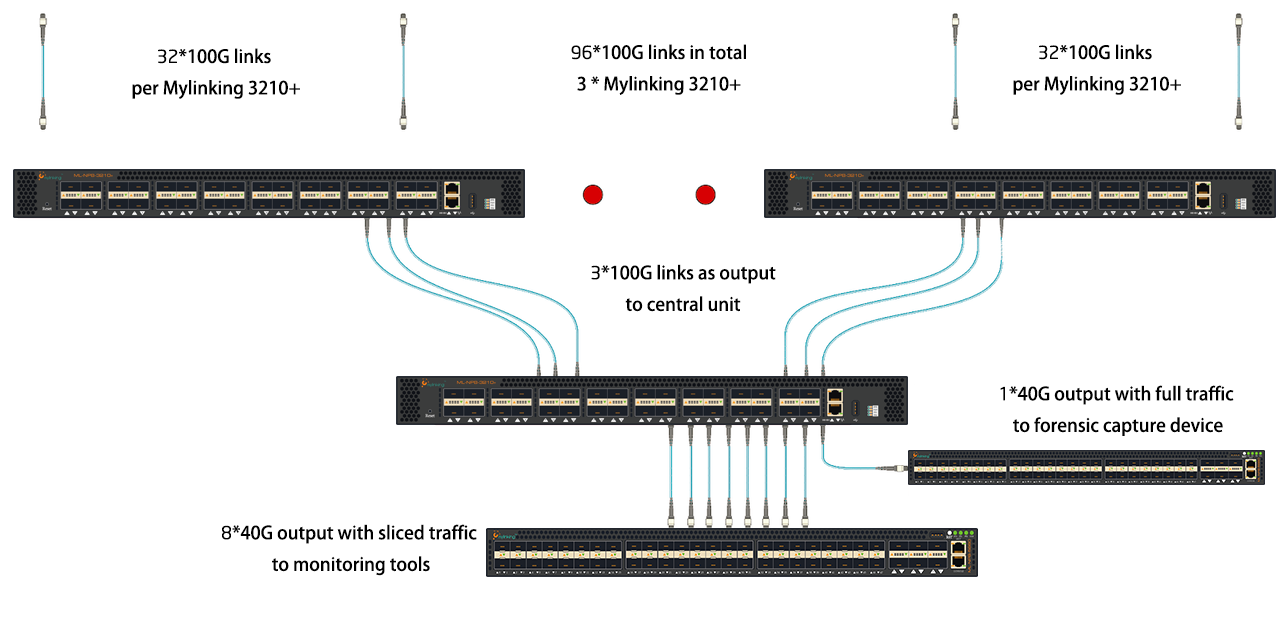
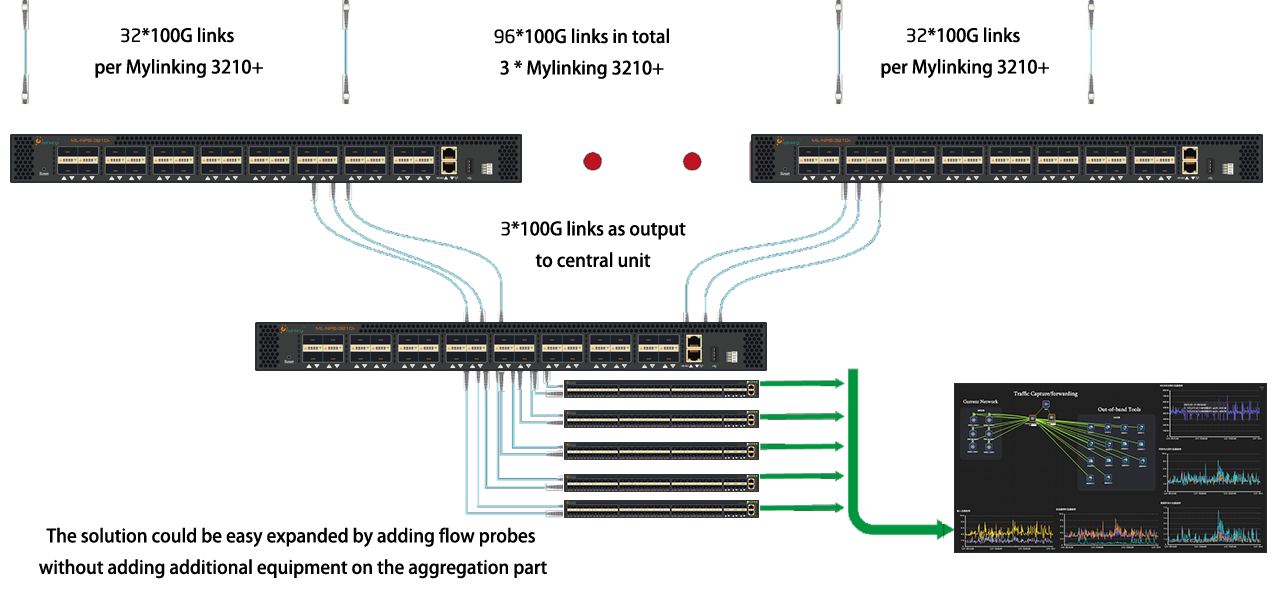
Customer requirements: Data centers monitor 96x100Gbit links with VXLAN
Technical challenges: Increasing network speeds require tools that can keep up with changing demands and make data centers highly reliable. Network visualization tools are needed to provide real-time, accurate analysis for network management and operations teams. The solution involves two issues:
Challenge 1: Aggregation in high bandwidth
Challenge 2: Being able to slice, tag, and VXLAN delete packets at multiples of 100Gbit line speeds of Mylinking Solutions: Slice Packets: Slice packets is the only way to save on monitoring equipment costs, as full bandwidth monitoring at this scale is beyond any budget. VXLAN deletion: The VXLAN deletion function saves bandwidth, and most monitoring tools cannot handle VXLANVLAN tagging: VLAN tagging is performed because customers require link-based reporting.
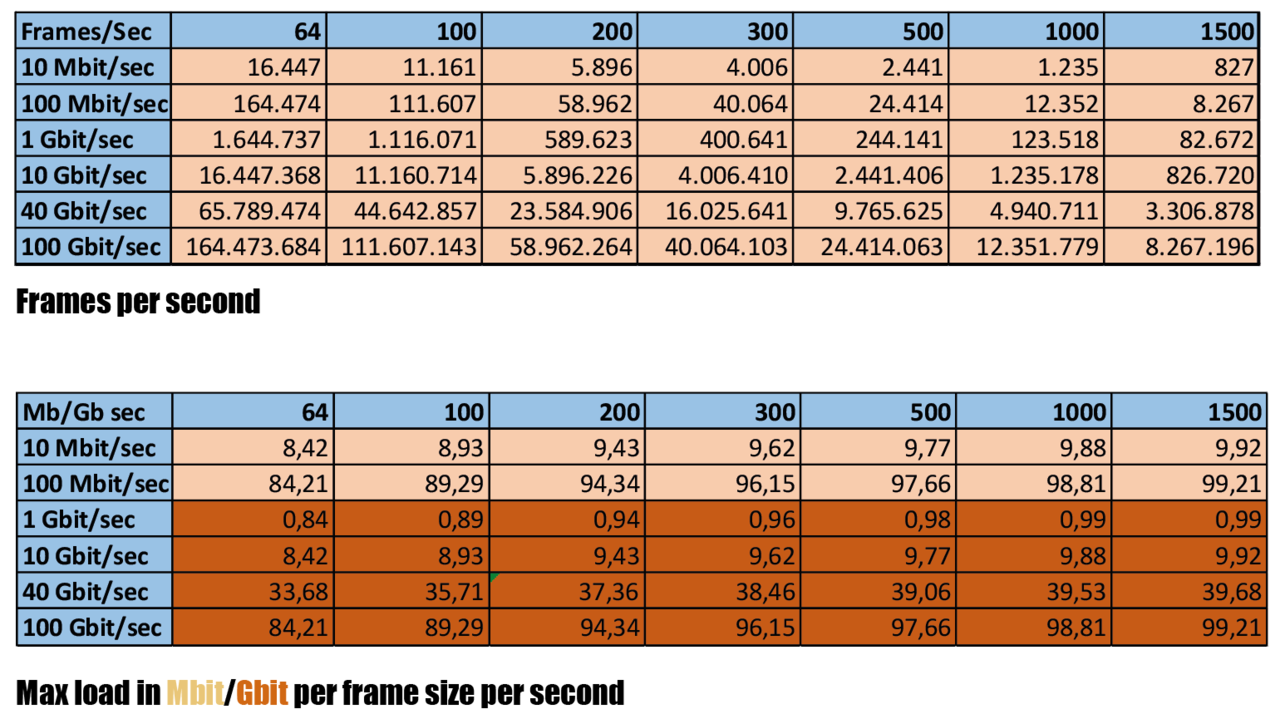
Packet slicing has the advantage of reducing the traffic load. Consider a typical load of 100 Ghit link 80/20% with an average packet size of 1000 bytes and 12 million packets per second (see table below). If you now cut packets into 100 bytes, which is enough for typical network monitoring, you can transfer 111 million packets on a 100 Ghi port and 44 million packets on a 40 Gbit port. Just monitor the load and the price of the tool and this is 4 or 10 times.
As a more advanced option, the Mylinking device can be connected in the second stage of the aggregation layer and can be fed a portion of the unsliced data to it for forensic capture.
This solution is possible because the performance of Mylinking ML-NPB-5660 is so good that a single device can easily handle the slicing of the entire traffic.
Post time: Aug-09-2023