In today's digital landscape, where internet access is ubiquitous, it's crucial to have robust security measures in place to protect users from accessing potentially malicious or inappropriate websites. One effective solution is the implementation of a Network Packet Broker (NPB) to monitor and control network traffic.
Let's walk through a scenario to understand how an NPB can be leveraged for this purpose:
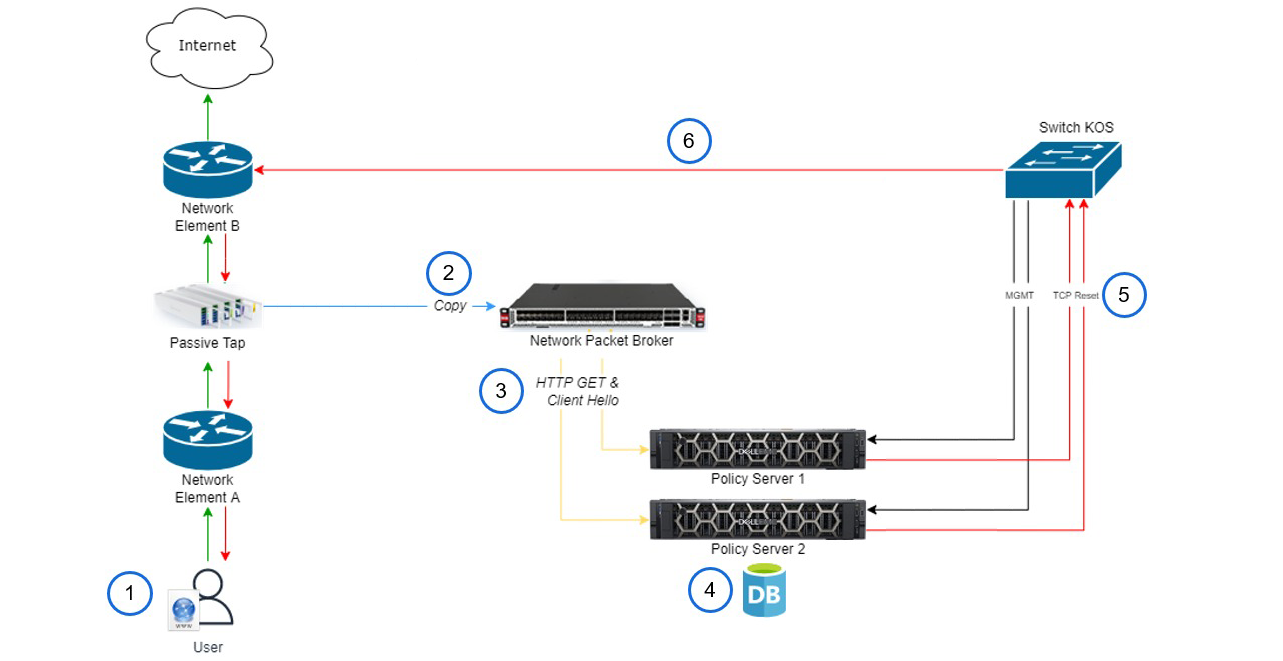
1- The user accesses a website: A user attempts to access a website from their device.
2- Packets passing through are replicated by a Passive Tap: As the user's request travels through the network, a Passive Tap replicates the packets, allowing the NPB to analyze the traffic without interrupting the original communication.
3- The Network Packet Broker forwards the following traffic to the Policy Server:
- HTTP GET: The NPB identifies the HTTP GET request and forwards it to the Policy Server for further inspection.
- HTTPS TLS Client Hello: For HTTPS traffic, the NPB captures the TLS Client Hello packet and sends it to the Policy Server to determine the destination website.
4- The Policy Server checks whether the accessed website is on the blacklist: The Policy Server, equipped with a database of known malicious or undesirable websites, checks if the requested website is on the blacklist.
5- If the website is on the blacklist, the Policy Server sends a TCP Reset packet:
- To the user: The Policy Server sends a TCP Reset packet with the source IP of the website and the destination IP of the user, effectively terminating the user's connection to the blacklisted website.
- To the website: The Policy Server also sends a TCP Reset packet with the source IP of the user and the destination IP of the website, cutting off the connection from the other end.
6- HTTP redirect (if the traffic is HTTP): If the user's request was made over HTTP, the Policy Server also sends an HTTP redirect to the user, redirecting them to a safe, alternative website.
By implementing this solution using a Network Packet Broker and a Policy Server, organizations can effectively monitor and control user access to blacklisted websites, protecting their network and users from potential harm.
Network Packet Broker (NPB) brings traffic from multiple sources for additional filtering to help balance traffic loads, traffic slicing, and masking capabilities. NPBs streamline the consolidation of network traffic originating from various sources, including routers, switches, and firewalls. This consolidation process creates a singular stream, simplifying the subsequent analysis and monitoring of network activities. These devices further facilitate targeted network traffic filtering, allowing organizations to focus on pertinent data for both analysis and security purposes.
In addition to their consolidation and filtering capabilities, NPBs exhibit intelligent network traffic distribution across multiple monitoring and security tools. This ensures that each tool receives the requisite data without inundating them with extraneous information. The adaptability of NPBs extends to optimizing the flow of network traffic, aligning with the unique capabilities and capacities of different monitoring and security tools. This optimization promotes the efficient utilization of resources throughout the network infrastructure.
The Network Packet Broker key advantages of this approach include:
- Comprehensive Visibility: The NPB's ability to replicate network traffic allows for a complete view of all communication, including both HTTP and HTTPS traffic.
- Granular Control: The Policy Server's capability to maintain a blacklist and take targeted actions, such as sending TCP Reset packets and HTTP redirects, provides granular control over user access to undesirable websites.
- Scalability: The NPB's efficient handling of network traffic ensures that this security solution can be scaled to accommodate growing user demands and network complexity.
By leveraging the power of a Network Packet Broker and a Policy Server, organizations can enhance their network security posture and safeguard their users from the risks associated with accessing blacklisted websites.
Post time: Jun-28-2024