Data masking on a network packet broker (NPB) refers to the process of modifying or removing sensitive data in network traffic as it passes through the device. The goal of data masking is to protect sensitive data from being exposed to unauthorized parties while still allowing network traffic to flow smoothly.
Why need Data Masking?
Because, to transform data "in the case of customer security data or some commercially sensitive data", request the data we want to transform is related to the security of user or enterprise data. To desensitize data is to encrypt such data to prevent leakage.
For the degree of data masking, generally speaking, as long as the original information can not be inferred, it will not cause information leakage. If too much modification, it is easy to lose the original characteristics of the data. Therefore, in the actual operation, you need to choose the appropriate desensitization rules according to the actual scenario. Change the name, ID number, address, mobile phone number, phone number and other customer related fields.
There are several different techniques that can be used for data masking on an NPB, including:
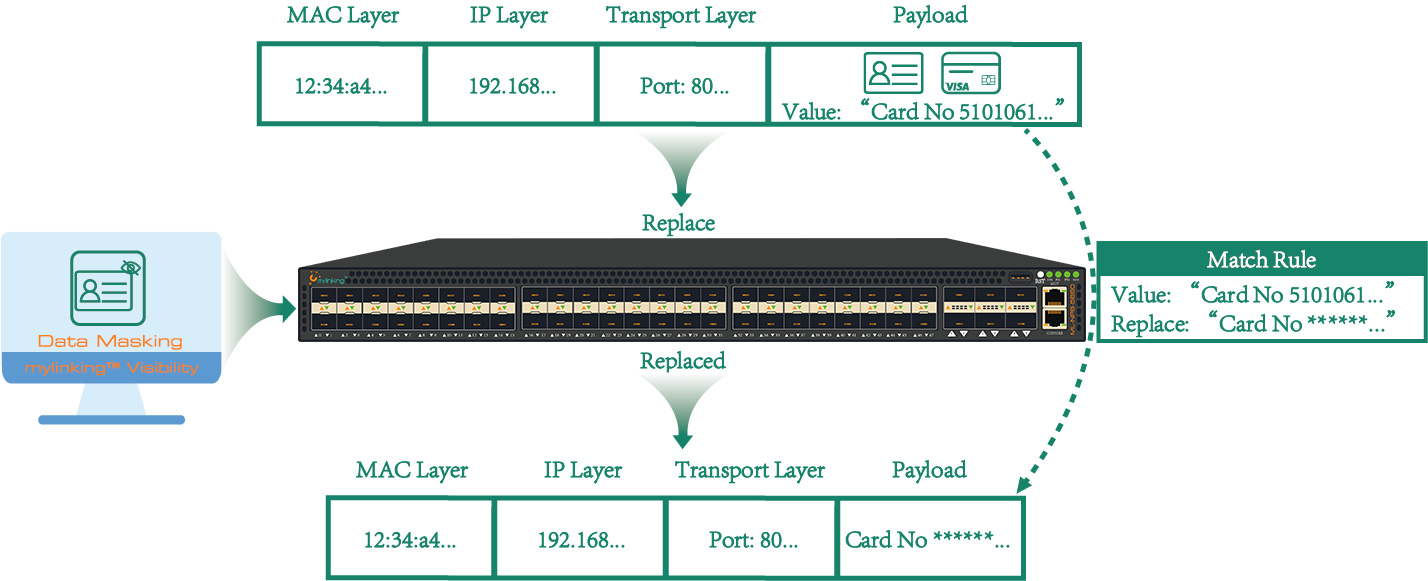
1. Tokenization: This involves replacing sensitive data with a token or placeholder value that has no meaning outside of the context of the network traffic. For example, a credit card number might be replaced with a unique identifier that is only associated with that card number on the NPB.
2. Encryption: This involves scrambling the sensitive data using an encryption algorithm, so that it cannot be read by unauthorized parties. The encrypted data can then be sent through the network as normal and decrypted by authorized parties on the other side.
3. Pseudonymization: This involves replacing the sensitive data with a different, but still recognizable value. For example, a person's name might be replaced with a random string of characters that is still unique to that individual.
4. Redaction: This involves completely removing the sensitive data from the network traffic. This can be a useful technique when the data is not needed for the intended purpose of the traffic and its presence would only increase the risk of a data breach.
The Mylinking™ Network Packet Broker (NPB) can support:
Tokenization: This involves replacing sensitive data with a token or placeholder value that has no meaning outside of the context of the network traffic. For example, a credit card number might be replaced with a unique identifier that is only associated with that card number on the NPB.
Pseudonymization: This involves replacing the sensitive data with a different, but still recognizable value. For example, a person's name might be replaced with a random string of characters that is still unique to that individual.
It can replace any key fields in the original data based on policy-level granularity to mask sensitive information. You can implement traffic output policies based on user configurations.
The Mylinking™ Network Packet Broker (NPB) "Network Traffic Data Masking" , also known as Network Traffic Data Anonymization, is the process of obscuring sensitive or personally identifiable information (PII) in network traffic. This can be done on a Mylinking™ Network Packet Proker (NPB) by configuring the device to filter and modify the traffic as it passes through.
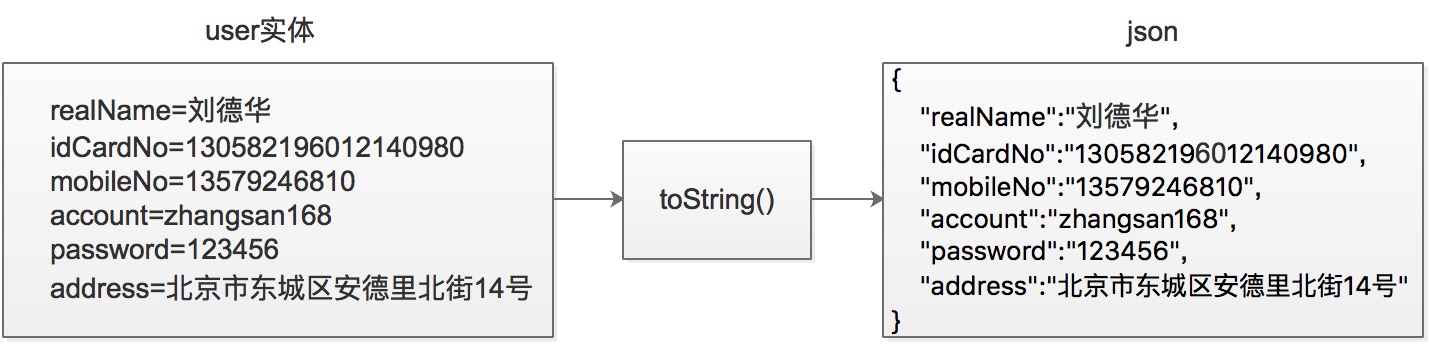
Before Data Masking:
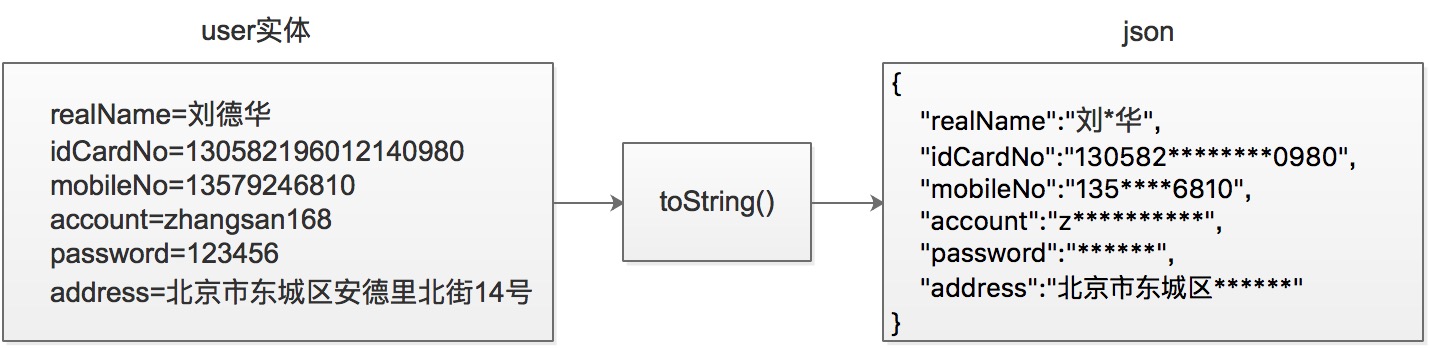
After Data Masking:
Here are the general steps to perform network data masking on a network packet broker:
1) Identify the sensitive or PII data that needs to be masked. This could include things like credit card numbers, social security numbers, or other personal information.
2) Configure the NPB to identify the traffic that contains the sensitive data using advanced filtering capabilities. This could be done using regular expressions or other pattern-matching techniques.
3) Once the traffic has been identified, configure the NPB to mask the sensitive data. This can be done by replacing the actual data with a random or pseudonymized value, or by removing the data altogether.
4) Test the configuration to ensure that the sensitive data is properly masked and that the network traffic still flows smoothly.
5) Monitor the NPB to ensure that the masking is being applied correctly and that there are no performance issues or other problems.
Overall, network data masking is an important step in ensuring the privacy and security of sensitive information on a network. By configuring a network packet broker to perform this function, organizations can minimize the risk of data breaches or other security incidents.
Post time: Apr-18-2023