Introduction
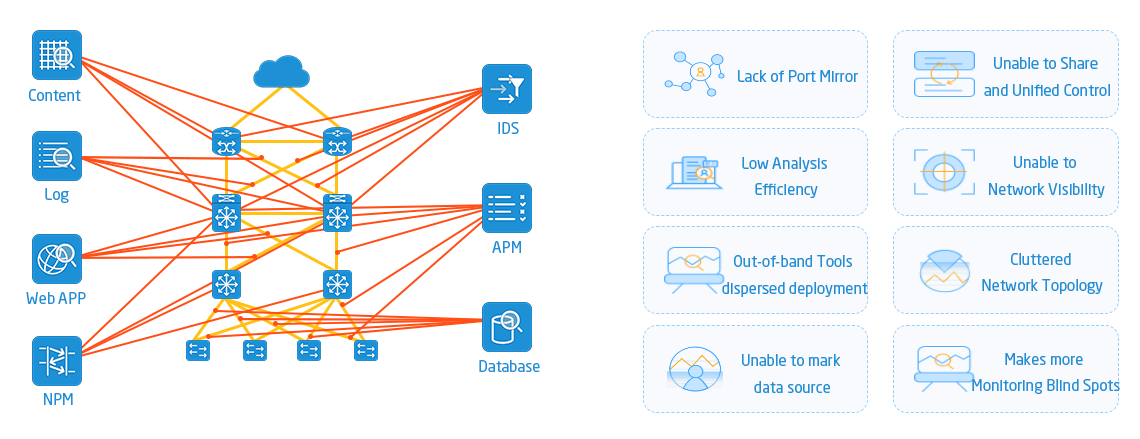
Network Traffic Collection and Analysis is the most effective means to obtain the first hand network user behavior indicators and parameters. With the continuous improvement of data center Q operation and maintenance, network traffic collection and analysis has become an indispensable part of the data center infrastructure. From the current industry use, network traffic collection is mostly realized by network equipment supporting bypass traffic mirror. Traffic collection needs to establish a comprehensive coverage, reasonable and effective traffic collection network, such traffic collection can help to optimize network and business performance indicators and reduce the probability of failure.
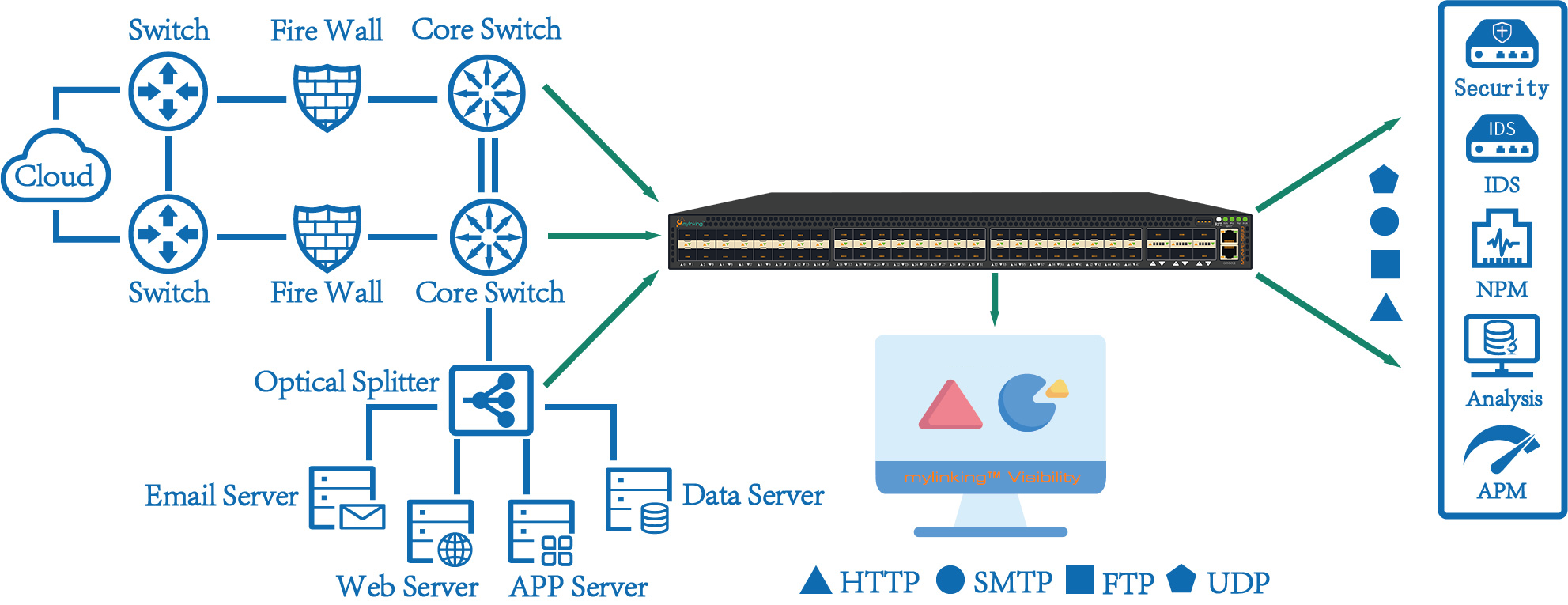
The traffic collection network can be regarded as an independent network composed of traffic collection devices and deployed in parallel with the production network. It collects the image traffic of each network device and aggregates the image traffic according to the regional and architectural levels. It uses the traffic filtering exchange alarm in the traffic acquisition equipment to realize the full line speed of the data for 2-4 layers of conditional filtering, removing duplicate packets, truncating packets and other advanced functional operations, and then sends the data to each traffic analysis system. The traffic collection network can accurately send specific data to each device according to the data requirements of each system, and solve the problem that the traditional mirror data cannot be filtered and sent, which consumes the processing performance of network switches. At the same time, the traffic filtering and exchange engine of the traffic collection network realizes the filtering and forwarding of data with low delay and high speed, ensures the quality of data collected by the traffic collection network, and provides a good data foundation for the subsequent traffic analysis equipment.
In order to reduce the impact on the original link, a copy of the original traffic is usually obtained by means of beam splitting, SPAN or TAP.
Passive Network Tap(Optical Splitter)
The way of using light splitting to obtain traffic copy requires the aid of a light splitter device. The light splitter is a passive optical device that can redistribute the power intensity of the optical signal in accordance with the required proportion. The splitter can divide light from 1 to 2,1 to 4 and 1 to multiple channels. In order to reduce the impact on the original link, the data center usually adopts the optical splitting ratio of 80:20, 70:30, in which 70,80 proportion of the optical signal is sent back to the original link. At present, optical splitters are widely used in network performance analysis (NPM/APM), audit system, user behavior analysis, network intrusion detection and other scenarios.
Advantages:
1. High reliability, passive optical device;
2. Does not occupy the switch port, independent equipment, subsequent can be good expansion;
3. No need to modify the switch configuration, no impact on other equipment;
4. Full traffic collection, no switch packet filtering, including error packets, etc.
Disadvantages:
1. The need for simple network cutover, backbone link fiber plug and dial to the optical splitter, will reduce the optical power of some backbone links
SPAN(Port Mirror)
SPAN is a feature that comes with the switch itself, so it just needs to be configured on the switch. However, this function will affect the performance of the switch and cause packet loss when the data is overloaded.
Advantages:
1. It is not necessary to add additional equipment, configure the switch to increase the corresponding image replication output port
Disadvantages:
1. Occupy the switch port
2. Switches need to be configured, which involves joint coordination with third-party manufacturers, increasing the potential risk of network failure
3. Mirror traffic replication has an impact on port and switch performance.
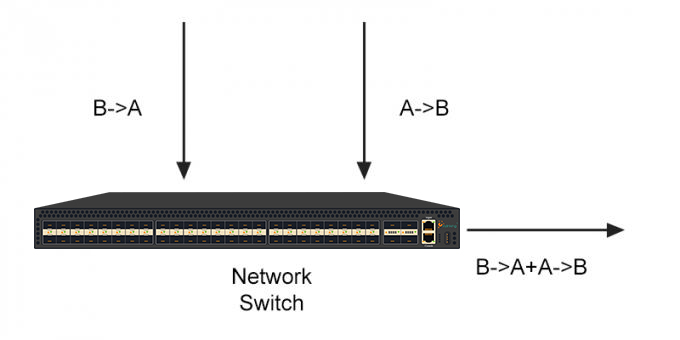
Active Network TAP (TAP Aggregator)
A Network TAP is an external network device that enables port mirroring and creates a copy of traffic for use by various monitoring devices. These devices are introduced at a place in the network path that needs to be observed, and it copies the data IP packets and sends them to the network monitoring tool. The choice of the access point for the Network TAP device depends on the focus of the network traffic -data collection reasons, routine monitoring of analysis and delays, intrusion detection, etc. Network TAP devices can collect and mirror data streams at 1G rate up to 100G.
These devices access traffic without the network TAP device modifying the packet flow in any way, regardless of the data traffic rate. This means that network traffic is not subject to monitoring and port mirroring, which is essential for maintaining the integrity of the data when routing it to security and analysis tools.
It ensures that the network peripheral devices monitor the traffic copies so that the network TAP devices act as observers. By feeding a copy of your data to any/all connected devices, you get full visibility at the network point. In the event that a network TAP device or monitoring device fails, you know that traffic will not be affected, ensuring that the operating system remains safe and available.
At the same time, it becomes the overall target of network TAP devices. Access to packets can always be provided without interrupting traffic in the network, and these visibility solutions can also address more advanced cases. The monitoring needs of tools ranging from next generation firewalls to data leakage protection, application performance monitoring, SIEM, digital forensics, IPS, IDS and more, force network TAP devices to evolve.
In addition to providing a complete copy of the traffic and maintaining availability, TAP devices can provide the following.
1. Filter Packets to Maximize Network Monitoring Performance
Just because a Network TAP device can create a 100% copy of a packet at some point does not mean that every monitoring and security tool needs to see the whole thing. Streaming traffic to all network monitoring and security tools in real time will only result in overordering, thus hurting the performance of the tools and the network in the process.
Placing the right Network TAP device can help filter packets when routed to the monitoring tool, distributing the right data to the right tool. Examples of such tools include Intrusion detection systems (IDS), data loss Prevention (DLP), security information and event management (SIEM), forensic analysis, and many more.
2. Aggregate Links for Efficient Networking
As Network Monitoring and Security requirements increase, network engineers must find ways to use existing IT budgets to accomplish more tasks. But at some point, you can't keep adding new devices to the stack and increasing the complexity of your network. It is essential to maximize the use of monitoring and security tools.
Network TAP devices can help by aggregating multiple network traffic, eastbound and westbound, to deliver packets to connected devices through a single port. Deploying visibility tools in this way will reduce the number of monitoring tools required. As East-West data traffic continues to grow in data centers and between data centers, the requirement for network TAP devices is essential to maintain visibility of all dimensional flows across large volumes of data.
Related article you may interesting, please visit here: How to Capture Network Traffic? Network Tap vs Port Mirror
Post time: Oct-24-2024